The Rise of AI Agents in Modern Development
The software development landscape is undergoing a seismic shift with the emergence of AI Agents. These autonomous systems are not just another tool in the developer's toolkit—they represent a fundamental change in how we approach problem-solving, automation, and intelligent system design. For enterprise developers and technical leaders, understanding AI Agents is becoming crucial for maintaining competitive advantage and driving strategic growth.
AI Agents combine the power of large language models, decision-making capabilities, and tool integration to create systems that can understand context, make autonomous decisions, and execute complex tasks. As organizations increasingly seek ways to accelerate development cycles and enhance operational efficiency, AI Agents have emerged as a key component of modern technology strategy.
Understanding AI Agents: A Technical Deep Dive
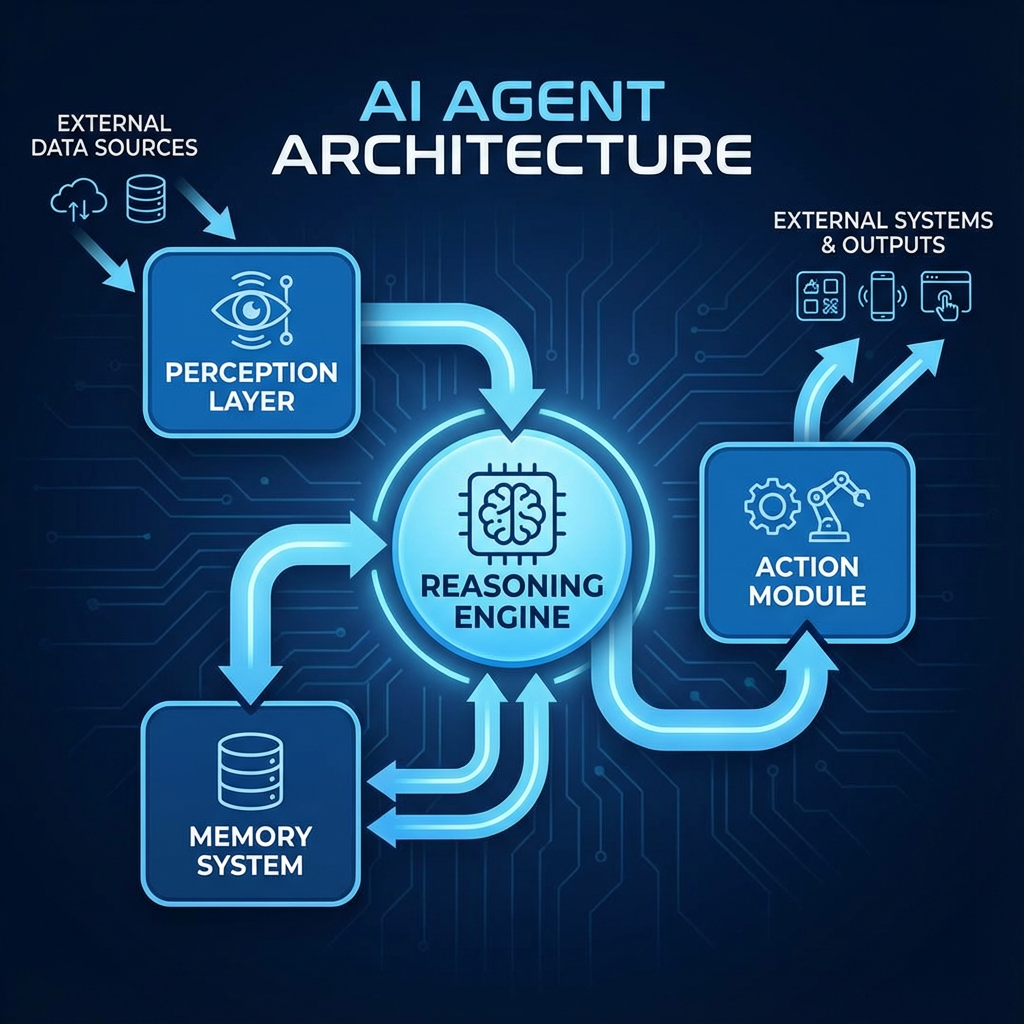
At their core, AI Agents are computational entities that perceive their environment, reason about goals, and take actions to achieve those goals. Unlike traditional software that follows predetermined instructions, AI Agents exhibit adaptive behavior and can operate with varying degrees of autonomy.
Key Technical Components
Perception Layer: AI Agents utilize various input mechanisms to understand their environment. This includes natural language processing for text inputs, API integrations for system data, and sensory inputs for physical or virtual environments. The perception layer transforms raw data into structured information that the agent can process.
Reasoning Engine: This is where the agent's intelligence resides. Using techniques ranging from rule-based systems to advanced neural networks, the reasoning engine evaluates situations, considers available actions, and determines optimal courses of action. Modern AI Agents typically leverage large language models (LLMs) for sophisticated reasoning capabilities.
Action Module: Once decisions are made, the action module executes them. This could involve API calls, database operations, code generation, or interactions with other systems. The action module must handle error scenarios, manage state, and ensure reliable execution.
Memory System: Effective AI Agents maintain both short-term and long-term memory. Short-term memory handles current context and immediate tasks, while long-term memory stores learned patterns, historical data, and accumulated knowledge that improves performance over time.
Architecture Patterns for AI Agent Systems
Building robust AI Agent systems requires careful architectural planning. Several patterns have emerged as best practices in the industry:
The Multi-Agent Architecture
This approach involves multiple specialized agents working together, each handling specific aspects of a complex task. For example, in a code review system, one agent might focus on security vulnerabilities, another on performance optimization, and a third on code style compliance. This modular approach enables better scalability and maintainability.
The Hierarchical Agent Model
In this pattern, higher-level agents coordinate and delegate tasks to subordinate agents. This structure is particularly effective for complex workflows that require both strategic planning and tactical execution. The hierarchy allows for clear separation of concerns and efficient resource allocation.
The Swarm Intelligence Approach
Inspired by natural systems, this architecture employs numerous simple agents that collectively exhibit intelligent behavior. Each agent follows simple rules, but their interactions create emergent intelligence. This pattern excels in scenarios requiring distributed problem-solving and adaptive behavior.
Current Applications in Software Development
AI Agents are already transforming various aspects of the software development lifecycle:
Automated Code Generation and Refactoring
Modern AI Agents can analyze existing codebases, understand architectural patterns, and generate new code that aligns with established conventions. They can identify refactoring opportunities, suggest optimizations, and even implement changes autonomously. This capability significantly accelerates development velocity while maintaining code quality.
Intelligent Testing and Quality Assurance
AI Agents revolutionize testing by creating comprehensive test suites, identifying edge cases, and adapting test strategies based on application changes. They can perform exploratory testing, generate realistic test data, and continuously monitor application performance in production environments.
DevOps Automation
From deployment pipelines to infrastructure management, AI Agents handle complex operational tasks with minimal human intervention. They can predict system failures, automatically scale resources, and optimize configurations based on real-time performance metrics.
Documentation and Knowledge Management
AI Agents automatically generate and maintain technical documentation, create API specifications, and build knowledge bases from code comments and commit messages. They ensure documentation stays synchronized with code changes, reducing the cognitive load on development teams.
Implementation Challenges and Best Practices
While AI Agents offer tremendous potential, implementing them effectively requires addressing several challenges:
Reliability and Predictability
AI Agents can sometimes produce unexpected results or fail to complete tasks reliably. Mitigation strategies include:
Implementing comprehensive validation frameworks
Creating fallback mechanisms for critical operations
Establishing clear boundaries for agent autonomy
Developing robust monitoring and alerting systems
Security and Compliance
Autonomous agents introduce new security considerations:
Implementing strict access controls and authentication mechanisms
Creating audit trails for all agent actions
Ensuring compliance with data protection regulations
Regular security assessments of agent behavior patterns
Integration Complexity
Connecting AI Agents with existing systems requires careful planning:
Designing standardized interfaces and protocols
Creating abstraction layers for system interactions
Implementing graceful degradation for service dependencies
Establishing clear data flow and transformation rules
Performance Optimization
AI Agents can be resource-intensive:
Implementing efficient caching strategies
Optimizing model inference processes
Balancing accuracy with computational costs
Designing scalable deployment architectures
Future Trends and Growth Opportunities
The AI Agent landscape continues to evolve rapidly, with several trends shaping the future:
Enhanced Multimodal Capabilities
Next-generation AI Agents will seamlessly process and generate text, images, audio, and video. This multimodal approach will enable more sophisticated interactions and broader application scopes, from creative content generation to complex data analysis.
Improved Reasoning and Planning
Advances in reasoning architectures will enable AI Agents to handle increasingly complex problems with better consistency and reliability. Techniques like chain-of-thought prompting, self-reflection, and iterative refinement will become standard features.
Collaborative Agent Ecosystems
The future will see standardized protocols enabling agents from different providers to collaborate effectively. This interoperability will create rich ecosystems where specialized agents can be combined to solve complex business problems.
Edge Deployment and Real-time Processing
As edge computing capabilities advance, AI Agents will increasingly operate locally on devices, reducing latency and improving privacy. This shift will enable real-time decision making in critical applications.
Autonomous Learning and Adaptation
Future AI Agents will continuously learn from their interactions and automatically improve their performance. This self-improvement capability will reduce the need for manual tuning and enable more adaptive systems.
Strategic Implications for Development Teams
For enterprise development teams, the rise of AI Agents represents both challenges and opportunities:
Skill Evolution
Developers will need to expand their skill sets to include AI Agent design, prompt engineering, and system integration. Traditional programming skills remain valuable but must be complemented with AI-specific expertise.
Process Transformation
Development methodologies will evolve to incorporate AI Agent capabilities. Agile practices will need adaptation to handle autonomous agents, and new metrics will emerge to measure agent productivity and effectiveness.
Organizational Structure
Teams may reorganize to include specialized roles like AI Agent architects, prompt engineers, and autonomous system validators. Cross-functional collaboration will become even more critical as AI Agents bridge technical and business domains.
Getting Started with AI Agent Development
For organizations looking to leverage AI Agents, a strategic approach is essential:
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning
Identify high-impact use cases within your organization
Evaluate existing systems for integration opportunities
Define success metrics and ROI expectations
Assess team capabilities and identify skill gaps
Phase 2: Pilot Implementation
Start with well-defined, bounded problems
Implement monitoring and observability from day one
Create feedback loops for continuous improvement
Document lessons learned and best practices
Phase 3: Scale and Optimize
Expand successful pilots to broader applications
Develop reusable agent components and patterns
Implement governance frameworks for agent deployment
Continuously optimize based on performance data
Conclusion: Embracing the AI Agent Revolution
AI Agents represent a fundamental shift in how we approach software development and automation. They offer unprecedented opportunities for accelerating development, improving quality, and creating more intelligent systems. However, realizing these benefits requires thoughtful strategy, careful implementation, and continuous learning.
For enterprise developers and technical leaders, now is the time to begin exploring AI Agent capabilities. Start small, learn quickly, and scale based on proven results. The organizations that master AI Agent technology will gain significant competitive advantages and position themselves for sustained growth in the evolving digital landscape.
The journey into AI Agents is not just about adopting new technology—it's about reimagining what's possible in software development. By embracing these powerful tools and approaches, development teams can unlock new levels of productivity, innovation, and business value.
Ready to dive deeper into AI Agent development? Explore our comprehensive resources and start building the future of intelligent automation today.